Not everyone is a Tableau guru, at least not yet. To help Tableau rookies, we’re starting from square one with the Tableau Essentials blog series. The series is intended to be an easy-to-read reference on the basics of using Tableau Software, particularly Tableau Desktop. Since there are so many cool features to cover in Tableau, the series will include several different posts.
Not everyone is a Tableau guru, at least not yet. To help Tableau rookies, we’re starting from square one with the Tableau Essentials blog series. The series is intended to be an easy-to-read reference on the basics of using Tableau Software, particularly Tableau Desktop 8.1 and 8.2. Since there are so many cool features to cover in Tableau, the series will include several different posts. This is the tenth post in the series. Check out the full list on our Tableau Essentials blog channel. This is also the third post in the Calculated Fields sub-series.
Today, we’ll dig into another group of functions used for Tableau’s calculated fields. In part one, we looked at Logical Functions. For part two, we’ll examine Number Functions.
To start, let’s go back to the Calculated Fields window. Right-click in the sidebar (a.k.a. Data window) and select Create Calculated Field:
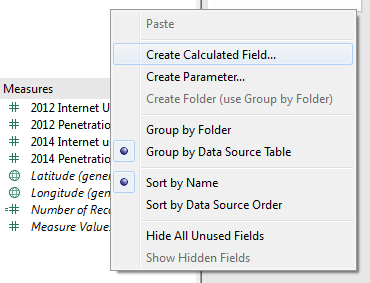
In the Calculated Field window, select Number from the Functions drop-down menu:
![]()
DEGREES Function
DEGREES(number)
This function converts the number or field from radians to degrees. For example:
![]()
EXP Function
EXP(number)
The number e is the base of the natural logarithm. This function returns e raised to the power of the number, i.e. e^5 would be expressed as:
![]()
LN Function
LN(number)
This function returns the natural log of the number. If the number is less than or equal to zero, it will return NULL. Example:
![]()
LOG Function
LOG(number,[base])
LOG returns the log of the number for the given base. If no base is provided, it will use base 10 by default. Example:
![]()
PI Function
PI()
This function returns the numeric constant of pi.
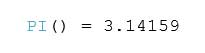
POWER Function
POWER(number, function)
The POWER function raises the number to the specified power. Example:
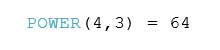
RADIANS Function
RADIAN(number)
This function converts the number from degrees to radians.
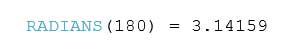
ROUND Function
ROUND(number,[decimals])
This function rounds the number to the nearest integer or to a specified number of decimal places. Example:
![]()
SIGN Function
SIGN(number)
The SIGN function returns the sign of a number. For positive numbers, the function returns a 1. For zero, it returns a 0. And for negative numbers, it returns a -1. Example:
![SIGN([Revenue]) = -1](/wp-content/uploads/sites/default/files/TECFNumber12.jpg)
SQRT Function
SQRT(number)
The SQRT function returns the square root of a number. Example:
![]()
SQUARE Function
SQUARE(number)
SQUARE returns the square of a number. Example:
![]()
ZN Function
ZN(expression)
The ZN function evaluates the expression, and if it is NULL, then it will return a value of 0. Otherwise, the expression is returned as stated. Example:
![]()
Statistical
MAX Function
MAX(number, number)
The MAX function returns the maximum of a single expression across all records or the maximum of two expressions for each record. The two arguments must be the same type. This function will return a value of NULL if either argument is NULL. Example:
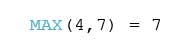
MIN Function
MIN(number, number)
Similar to the MAX function, the MIN function returns the minimum of a single expression across all records or the minimum of two expressions for each record. MIN returns a value of NULL if either of the two arguments is NULL. The two arguments must be of the same type. For example:
![]()
Trigonometric
ACOS Function
ACOS(number)
This function returns the arc cosine of a number. The result is in radians. Example:
![]()
ASIN Function
ASIN(number)
ASIN returns the arc sine of a number. The result is in radians. Example:
![]()
ATAN Function
ATAN(number)
The ATAN function returns the arc tangent of a number. The result is in radians. Example:
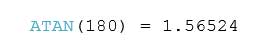
ATAN2 Function
ATAN2(y number, x number)
The ATAN2 function returns the arc tangent of two given numbers. The result is in radians. Example:
![]()
COS Function
COS(number)
COS returns the cosine of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example:
![]()
COT Function
COT(number)
This function returns the cotangent of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example:

SIN Function
SIN(number)
The SIN function returns the sine of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example:
![]()
TAN Function
TAN(number)
This function returns the tangent of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example:
![]()
Depending on the nature of your reporting and your business, you many need to use Number Functions routinely or not at all. If you do need to use them or just wish to experiment to build your knowledge, Tableau will offer help when you click on any of these functions. A brief introduction and example of the function will be presented in the lower right-hand box on the Calculated Fields window.
Calculated Fields
Calculated fields can add a whole new layer of insight to your Tableau dashboards. The possibilities are practically endless, but we’ll be covering the fundamentals, especially functions, to help you build a foundational understanding of how and when to use them. Check back for more posts covering:
- Logical Functions
- Number Functions
- Date Functions
- String Functions
- Type Conversion
- Aggregate Functions
- User Functions
Another great resource for functions is Dan Murray’s best-selling guidebook, “Tableau Your Data!” It features a whole section devoted the functions we’ll be covering in this series and much, much more.
More Tableau Essentials
Want to learn more about Tableau? We have several posts outlining all of Tableau’s fantastic features. Check out the full list on our Tableau Essentials blog channel.
As always, let us know if you have any questions or comments about this post or Tableau in general. If you’re looking for personalized training or help with something bigger, contact us directly!